type
status
date
slug
summary
tags
category
icon
password
Property
Aug 14, 2023 11:52 AM
本节内容
什么是委托
委托的声明(自定义委托)
委托的使用
什么是委托
委托(delegate)是函数指针的“升级版”
- 实例:C/C++中的函数指针
一切皆地址
- 变量(数据)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值
- 函数(算法)事以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令
直接调用与间接调用
- 直接调用:通过函数名来调用函数,CPU通过函数名直接获得函数所在地址开始执行→返回
- 间接调用:通过函数指针来调用函数,CPU通过读取函数指针存储的值获得函数所在地址并开始执行→返回
Java中没有与委托相对应的功能实体
委托的简单使用
- Action委托
- Func委托
程序=数据+算法
委托的声明(自定义委托)
委托是一种类(class),类是数据类型,所以委托也是一种数据类型
它的声明方式与一般的类不同,主要是为了照顾可读性和C/C++传统
鼠疫声明委托的位置
- 避免写错地方结果声明成嵌套类型
委托与所封装的方法必须“类型兼容”

- 返回值的数据类型一致
- 参数列表在数个和数据类型上一致(参数名不需要一样)
委托需要生命在名称空间体里面
委托的一般使用
实例:把方法当做参数传给另一个方法
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用”制定的外部方法来产生结果
- 相当于“填空题”
- 常位于代码中部
- 委托有返回值
- 正确使用2:回调(callback)方法,调用指定的外部方法
- 相当于流水线
- 常位于代码末尾
- 委托无返回值
注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大的东西,一旦被滥用则会后果非常严重
- 缺点1:这是一种方法级别的紧耦合,在工作中要慎之又慎
- 缺点2:使可读性下降,debug难度增加
- 缺点3:把委托回调,异步调用和多线程纠缠在一起,会让代码变得难以阅读和维护
- 缺点4:委托使用不当可能造成内存泄漏和程序性能下降
良好的复用结构是所有优秀软件所追求的共同目标之一
模板方法
回调方法
没有返回值的方法,使用Action委托
委托的高级使用
多播(multicast)委托
隐式异步调用
- 同步与异步的简介
- 中英文的语言差异
- 同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
- 异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的同步进行)
- 同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 每一个运行的程序是一个进程(process)
- 每个进程可以有一个或多个线程(thread)
- 同步调用是在同一个线程内
- 异步调用的底层机理是多线程
- 穿行==同步==单线程,并行==异步==多线程
- 隐式多线程vs显示多线程
- 直接同步调用:使用方法名
- 间接同步调用:使用单播、多播委托的invoke方法
- 隐式异步调用:使用委托的BeginInvoke
- 现实异步调用:使用Thread或Task
应该适时地使用接口(interface)取代一些堆委托的使用
- Java完全地使用接口取代了委托的功能,即java没有与C#中委托相对应的功能实体
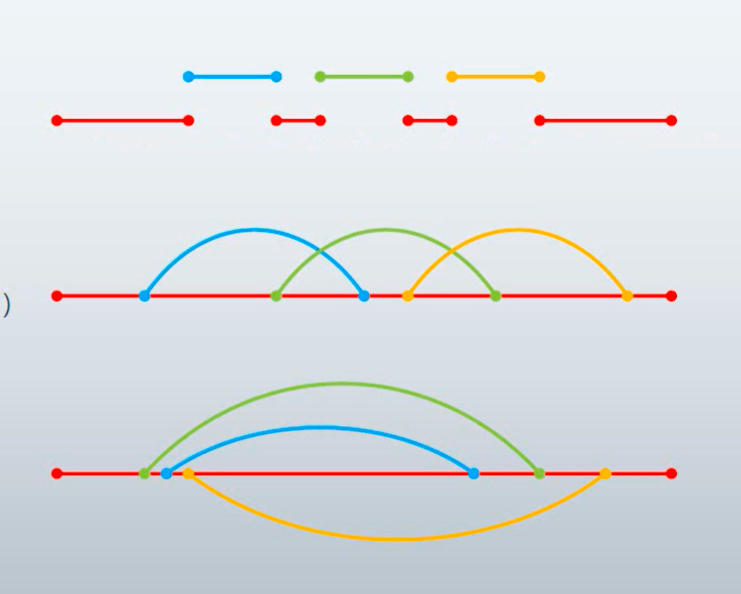
同步1
直接调用是同步的
间接调用也是同步的
单播也是,多播也是
委托的隐式异步调用
beginInvoke方式
结果
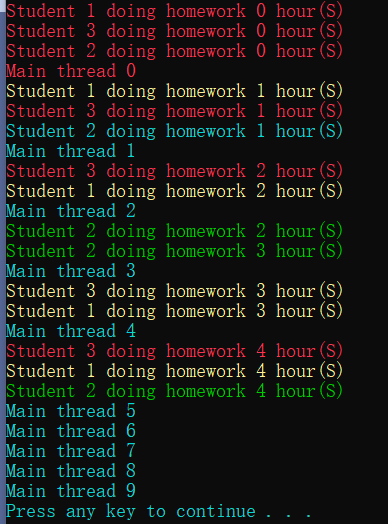
打印的颜色有的一样,这就是争抢前景色的资源,发生冲突
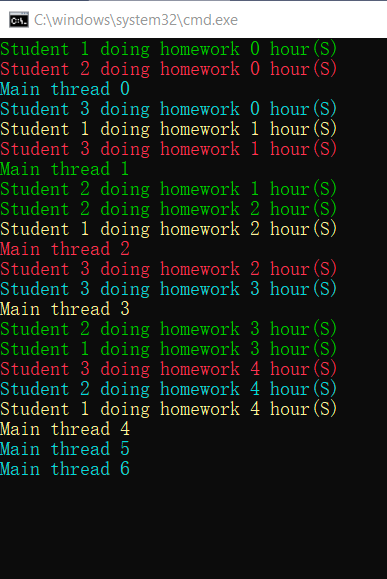
显示的异步调用,手动声明多线程
一种为使用thread
结果
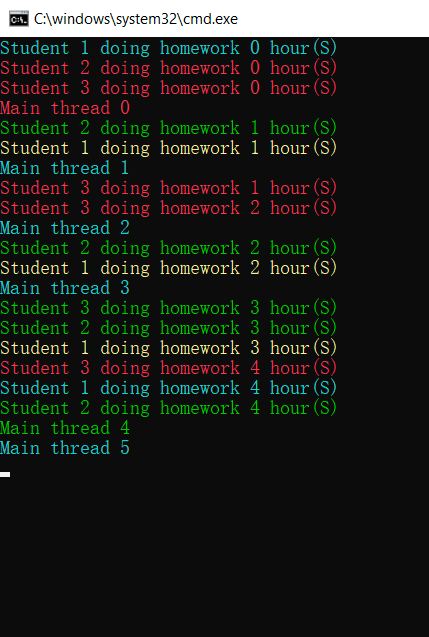
另一种为使用Task的方式
结果
使用接口取代委托
重构基本不改变原来的代码,只是把原来的代码放到更合适的地方去
- 作者:Kitety
- 链接:https://www.kitety.com/article/C-sharp-leraning-delegation-details
- 声明:本文采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处。
相关文章
